Understanding Vasovagal Syncope: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment

Vasovagal syncope is a fairly common condition that affects individuals of all ages and backgrounds. It is characterized by a sudden loss of consciousness, usually accompanied by a temporary drop in blood pressure and a slow heart rate. In this article, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview of vasovagal syncope, including its causes, symptoms, and available treatment options.
What is Vasovagal Syncope?
Vasovagal syncope, also known as fainting or neurocardiogenic syncope, occurs when there is a sudden and temporary disruption in the body’s autonomic nervous system. This disruption can lead to a decrease in blood flow to the brain, resulting in a loss of consciousness. The episode is typically brief and individuals usually regain consciousness on their own.
Defining Vasovagal Syncope
Vasovagal syncope is a type of reflex syncope, which means it is triggered by certain stimuli. The most common triggers include emotional stress, pain, fear, standing for long periods, or sudden changes in body position. The exact mechanisms behind these triggers are not fully understood, but it is believed that they cause a sudden shift in the body’s autonomic balance, leading to a temporary loss of consciousness.
Prevalence and Demographics
Vasovagal syncope is a relatively common condition, affecting people of all ages and genders. It is estimated that up to 30% of the general population will experience at least one episode of vasovagal syncope in their lifetime. The condition is more common in younger individuals, with peak prevalence occurring in adolescence and early adulthood. It also tends to occur more frequently in females compared to males.
While vasovagal syncope is generally considered benign and not life-threatening, it can still have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life. The unpredictability of when an episode may occur can lead to anxiety and fear of fainting in social situations or during activities that require standing for extended periods.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The symptoms of vasovagal syncope can vary from person to person but often include dizziness, lightheadedness, nausea, sweating, and a sudden feeling of warmth. In some cases, individuals may experience visual disturbances or ringing in the ears before losing consciousness. Diagnosis of vasovagal syncope is typically based on a thorough medical history, physical examination, and may involve additional tests such as a tilt table test or an electrocardiogram to rule out other potential causes of fainting.
The Physiology Behind Vasovagal Syncope
To understand why vasovagal syncope occurs, it is important to have a basic understanding of the body’s autonomic nervous system. The autonomic nervous system is responsible for regulating various automatic bodily functions, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and digestion.
Vasovagal syncope, also known as neurocardiogenic syncope, is a common cause of fainting episodes. It occurs when there is a sudden drop in blood pressure, resulting in decreased blood flow to the brain. This can lead to a temporary loss of consciousness and a feeling of lightheadedness or dizziness.
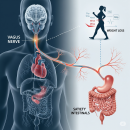
The Role of the Vagus Nerve
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve, plays a crucial role in the development of vasovagal syncope. This nerve helps regulate heart rate, blood pressure, and blood vessel dilation. In individuals prone to vasovagal syncope, the vagus nerve can become overactive, leading to a sudden drop in blood pressure and decreased blood flow to the brain.
Furthermore, the vagus nerve is involved in the body’s parasympathetic response, which is responsible for rest and digestion. When the vagus nerve is overstimulated, it can trigger a vasovagal response, causing a decrease in heart rate and blood pressure.
The Body’s Response to Stress
During periods of stress or heightened emotional states, the body releases stress hormones such as adrenaline. These hormones can affect the autonomic nervous system and trigger a response that leads to vasovagal syncope. The exact mechanisms involved in this response are still being studied, but it is thought to involve a combination of hormonal changes and altered blood flow dynamics.
In addition to stress, other triggers for vasovagal syncope include dehydration, prolonged standing, and extreme heat. These factors can exacerbate the body’s response and increase the likelihood of experiencing a fainting episode.
Identifying the Causes of Vasovagal Syncope
Vasovagal syncope can be caused by a variety of factors, ranging from external triggers to underlying health conditions. Identifying the underlying cause of vasovagal syncope is important for developing an effective treatment plan.
When investigating the causes of vasovagal syncope, it is essential to consider individual factors that may contribute to the condition. Factors such as age, gender, and overall health can play a role in the likelihood of experiencing vasovagal syncope. Understanding these unique aspects can provide valuable insight into the management and prevention of future episodes.
Common Triggers for Vasovagal Syncope
There are several common triggers that can lead to an episode of vasovagal syncope. Emotional stress, such as anxiety, fear, or panic, can elicit a fainting response in susceptible individuals. Additionally, standing for long periods, sudden changes in body position, extreme heat, or the sight of blood can also trigger an episode.
It is important to note that triggers for vasovagal syncope can vary from person to person. While some individuals may experience fainting in response to emotional stress, others may be more prone to episodes when exposed to specific environmental factors. Recognizing these individual triggers can aid in the development of personalized treatment strategies.
Underlying Health Conditions
In some cases, vasovagal syncope may be a symptom of an underlying medical condition. These conditions can include heart abnormalities, such as arrhythmias or structural defects, or neurological disorders that affect the autonomic nervous system. Identifying and addressing these underlying conditions is crucial for effective treatment.
Furthermore, certain medications or substances may also contribute to the occurrence of vasovagal syncope. Understanding the potential interactions between these external factors and the body’s physiological responses can help healthcare providers tailor treatment plans to address both the underlying cause and the triggering factors.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Vasovagal Syncope
Vasovagal syncope is characterized by a distinct set of symptoms that can help differentiate it from other causes of fainting. Recognizing these symptoms is important for proper diagnosis and management of the condition.
Understanding the triggers for vasovagal syncope can also aid in its recognition. Common triggers include prolonged standing, dehydration, extreme emotional distress, pain, and exposure to triggering sights or sounds. By identifying and avoiding these triggers, individuals with vasovagal syncope can potentially prevent episodes.
Physical Symptoms
During an episode of vasovagal syncope, individuals may experience lightheadedness, dizziness, blurred vision, nausea, sweating, and a pale complexion. Some individuals may also have muscle twitches or temporary loss of control over bodily functions.
It is important to note that the physical symptoms of vasovagal syncope can vary in intensity from person to person. While some individuals may only experience mild lightheadedness, others may have more severe symptoms such as vomiting or loss of consciousness.
Emotional and Cognitive Symptoms
In addition to the physical symptoms, individuals with vasovagal syncope may also experience emotional and cognitive changes. These can include feelings of fear or anxiety, confusion, and a sense of impending doom. These symptoms are often transient and resolve once consciousness is regained.
It is not uncommon for individuals with vasovagal syncope to feel fatigued or emotionally drained after an episode. This can be due to the stress and anxiety that often accompany fainting spells. Seeking support from healthcare providers, counselors, or support groups can be beneficial in managing the emotional aftermath of vasovagal syncope.
Diagnosing Vasovagal Syncope
Diagnosing vasovagal syncope involves a thorough medical history review, physical examination, and may require additional tests or procedures to rule out other causes of fainting.
Understanding the intricacies of vasovagal syncope is crucial in its diagnosis. This condition, characterized by a sudden drop in heart rate and blood pressure leading to temporary loss of consciousness, often occurs in response to triggers like emotional stress, pain, or standing for long periods. By delving deep into the patient’s medical history and conducting a comprehensive physical examination, healthcare providers can gather valuable insights into the frequency and nature of fainting episodes, aiding in accurate diagnosis.
Medical History and Physical Examination
During the medical history review, the healthcare provider will ask detailed questions about the episodes of fainting, including the circumstances surrounding the event and any potential triggers. A physical examination may also be conducted to check for any underlying health conditions that could contribute to vasovagal syncope.
Moreover, understanding the patient’s overall health status and lifestyle factors is essential in unraveling the underlying mechanisms of vasovagal syncope. Factors such as dehydration, medication side effects, or autonomic nervous system dysfunction can play a significant role in triggering syncope episodes, underscoring the importance of a holistic approach to diagnosis.
Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
In some cases, additional tests may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis of vasovagal syncope and rule out other potential causes. These tests can include electrocardiograms (ECGs) to evaluate heart rhythm, echocardiography to assess heart structure and function, or tilt table tests to provoke and evaluate the response to certain triggers.
Furthermore, advanced diagnostic tools like ambulatory monitoring devices or electrophysiological studies may be employed in complex cases to capture elusive fainting episodes and provide a more comprehensive understanding of the underlying cardiac abnormalities. By combining clinical expertise with cutting-edge technology, healthcare providers can offer tailored diagnostic approaches to effectively manage vasovagal syncope.
Treatment Options for Vasovagal Syncope
While vasovagal syncope can be a challenging condition to manage, there are several treatment options available to help individuals reduce the frequency and severity of episodes. Understanding these options can empower individuals to take control of their health and well-being.
It is important to note that treatment plans for vasovagal syncope are often personalized based on the individual’s specific triggers and medical history. Working closely with healthcare providers can help tailor a comprehensive approach to managing this condition effectively.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
Making certain lifestyle modifications can be beneficial for individuals with vasovagal syncope. These can include staying well-hydrated, avoiding known triggers, such as standing for long periods, and practicing stress reduction techniques, such as deep breathing exercises or meditation. Engaging in regular physical activity and maintaining a balanced diet can also contribute to overall cardiovascular health.
Furthermore, establishing a consistent sleep routine and prioritizing adequate rest can play a significant role in managing vasovagal syncope. Creating a supportive environment at home and work, where stressors are minimized, can help individuals better cope with potential triggers.
Medications and Therapies
In some cases, medications may be prescribed to help manage vasovagal syncope. These medications focus on regulating heart rate or blood pressure to prevent sudden drops. Additionally, biofeedback therapy or cognitive-behavioral therapy may be recommended to help individuals learn to recognize and control the early warning signs of an episode. These therapeutic approaches aim to enhance self-awareness and empower individuals to proactively address symptoms.
Exploring complementary therapies, such as acupuncture or yoga, can also complement traditional treatment methods for vasovagal syncope. These holistic approaches focus on promoting relaxation, improving circulation, and fostering a sense of balance within the body.
Surgical Interventions
In rare cases, surgical interventions may be considered for individuals with severe and refractory vasovagal syncope. These interventions can include the placement of a pacemaker to help regulate heart rate or cardiac ablation to disrupt the overactive vagus nerve signaling. Surgical options are typically reserved for individuals who have not responded to conservative treatments and require more aggressive management strategies.
It is essential for individuals with vasovagal syncope to work collaboratively with a multidisciplinary healthcare team, including cardiologists, neurologists, and psychologists, to address the complex nature of this condition comprehensively. By embracing a holistic approach to treatment, individuals can enhance their quality of life and minimize the impact of vasovagal syncope on their daily activities.
Living with Vasovagal Syncope
While vasovagal syncope can be disruptive and potentially dangerous, there are strategies and support systems available to help individuals manage the condition and improve their quality of life.
Vasovagal syncope, also known as neurocardiogenic syncope, is a common cause of fainting episodes. It occurs when the body overreacts to certain triggers, leading to a sudden drop in heart rate and blood pressure. These triggers can vary from person to person and may include stress, pain, dehydration, or even the sight of blood. Understanding these triggers and learning to manage them is key to living well with vasovagal syncope.
Coping Strategies and Support
Learning effective coping strategies can be crucial for individuals with vasovagal syncope. These strategies can include recognizing and avoiding triggers, practicing stress reduction techniques, and having a support system in place to help during episodes.
Support systems can come in various forms, such as educating family members and friends about the condition so they can provide assistance when needed. Additionally, joining support groups or online forums can connect individuals with others who are going through similar experiences, offering a sense of community and understanding.
Prognosis and Long-Term Management
With proper management and adherence to treatment plans, individuals with vasovagal syncope can lead normal and fulfilling lives. It is important to work closely with healthcare providers to develop a tailored treatment plan that addresses the specific needs of each individual.
Long-term management may involve lifestyle modifications, such as staying well-hydrated, avoiding triggers, and incorporating regular exercise into daily routines. In some cases, medications or medical procedures may be recommended to help control symptoms and prevent fainting episodes.
In conclusion, understanding vasovagal syncope requires knowledge of its causes, symptoms, and available treatment options. By recognizing the triggers, seeking appropriate medical care, and implementing lifestyle changes, individuals with vasovagal syncope can effectively manage their condition and live a fulfilling life.