The Importance of the Phrenic Nerve
The phrenic nerve is a crucial component of the body’s respiratory system, playing a vital role in allowing us to breathe effortlessly and efficiently. Its intricate network of signals and connections is often underestimated and overlooked, yet understanding its anatomy, function, and impact on overall health is essential.
Understanding the Phrenic Nerve
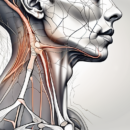
The phrenic nerve is one of the twelve pairs of cranial nerves originating from the spinal cord. It arises from the C3 to C5 nerve roots in the neck and descends vertically through the chest towards the diaphragm, the primary muscle responsible for breathing. Though essential for respiration, the phrenic nerve extends its influence beyond mere mechanical movements.
Expanding on the intricate network of the phrenic nerve, it is fascinating to note that this nerve plays a crucial role in the body’s reflex mechanisms. In addition to its primary function of regulating breathing, the phrenic nerve also interacts with the brainstem, contributing to the body’s ability to respond to various stimuli. This intricate interplay between the phrenic nerve and the central nervous system highlights the complexity of neural pathways involved in maintaining homeostasis.
Anatomy of the Phrenic Nerve
The phrenic nerve consists of a complex network of nerve fibers comprised of sensory, motor, and autonomic components. These fibers transmit signals between the brain and the diaphragm, ensuring the coordination required for effortless breathing. With its origin in the neck, the phrenic nerve travels through the thorax and contributes to a vast array of bodily functions beyond just respiratory control.
Delving deeper into the anatomy of the phrenic nerve, it is intriguing to explore the intricate connections it forms with neighboring structures in the body. Not only does the phrenic nerve innervate the diaphragm, but it also communicates with surrounding tissues and organs, playing a role in modulating responses to pain and inflammation. This extensive network underscores the phrenic nerve’s significance in orchestrating a harmonious symphony of physiological processes.
The Role of the Phrenic Nerve in the Body
Beyond facilitating breathing, the phrenic nerve has been implicated in other physiological processes. The nerve fibers connect with regions responsible for regulating heart rate and blood pressure, suggesting a potential role in cardiovascular health. Furthermore, recent studies have identified connections between the phrenic nerve and the immune system, indicating its involvement in the body’s defense mechanisms against infections and diseases.
Moreover, emerging research has shed light on the phrenic nerve’s role in neurological conditions, hinting at its potential implications in disorders such as sleep apnea and chronic pain syndromes. The intricate web of functions attributed to the phrenic nerve underscores its significance as not just a conductor of breathing but as a multifaceted player in the orchestra of human physiology.
The Phrenic Nerve and Respiratory Function
The intricate connection between the diaphragm and the phrenic nerve highlights the importance of this neural pathway in regulating breathing patterns and maintaining respiratory efficiency.
The phrenic nerve, arising from the cervical spine (C3-C5), plays a crucial role in the respiratory system by providing motor innervation to the diaphragm. This nerve is a mixed nerve, containing both motor and sensory fibers, allowing for the transmission of signals between the brain and the diaphragm. The phrenic nerve’s origin in the cervical spine makes it susceptible to injury in cases of trauma or certain medical conditions, leading to potential respiratory complications.
Connection Between the Diaphragm and the Phrenic Nerve
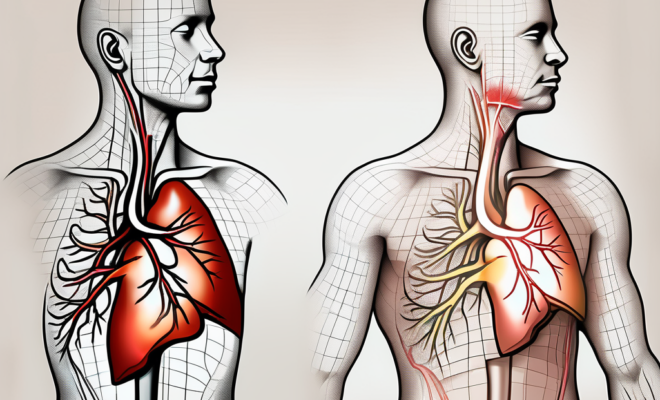
The diaphragm, the primary muscle that drives inhalation and exhalation, is innervated by the phrenic nerve. Multiple nerve branches extend to the diaphragm’s muscle fibers, ensuring coordination and synchronized contractions necessary for effective respiration. This intricate connection allows the diaphragm to contract and expand in harmony, creating the pressure changes required to draw air into the lungs.
In addition to its role in respiration, the phrenic nerve also plays a part in non-respiratory functions. It contributes to the innervation of the pericardium, the membrane surrounding the heart, and provides sensory information to the central nervous system. This dual functionality underscores the phrenic nerve’s significance beyond its involvement in breathing.
How the Phrenic Nerve Regulates Breathing
The coordinated signals from the phrenic nerve trigger the rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the diaphragm. During inhalation, the diaphragm contracts, expanding the chest cavity and drawing air into the lungs. Conversely, during exhalation, the diaphragm relaxes, allowing the lungs to release carbon dioxide. This intricate interplay between the phrenic nerve and the diaphragm ensures a steady supply of oxygen and the removal of waste gases, maintaining respiratory homeostasis.
Moreover, the phrenic nerve’s involvement in the regulation of breathing extends to its interaction with other respiratory muscles, such as the intercostal muscles. By coordinating the actions of multiple muscle groups, the phrenic nerve contributes to the complex process of breathing, highlighting its indispensable role in sustaining life-sustaining respiratory functions.
Disorders Related to the Phrenic Nerve
While the phrenic nerve is integral to respiratory function, it can be susceptible to certain disorders that may have debilitating effects on an individual’s quality of life.
The phrenic nerve, originating from the cervical nerves in the neck, plays a crucial role in controlling the movement of the diaphragm, the main muscle involved in breathing. Any disruption or damage to this nerve can significantly impact a person’s ability to breathe properly and may lead to various respiratory complications.
Symptoms of Phrenic Nerve Damage
Damage or injury to the phrenic nerve can lead to a range of respiratory issues. Common symptoms may include shortness of breath, decreased lung capacity, and weakened overall respiratory function. In more severe cases, individuals may experience difficulty with everyday activities and reduced exercise tolerance. Prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial in managing these symptoms and optimizing respiratory health.
Furthermore, phrenic nerve damage can also manifest as referred pain in the shoulder or neck, as the nerve shares connections with other areas of the body. This additional symptom can sometimes lead to misdiagnosis or delayed treatment, emphasizing the importance of thorough evaluation by healthcare professionals.
Treatment Options for Phrenic Nerve Disorders
While treatment options vary depending on the specific condition and severity, managing phrenic nerve disorders often involves a multidisciplinary approach. This can include physical therapy, respiratory exercises, medication, and, in some cases, surgical interventions. Seeking professional medical advice and guidance is vital to ensure an accurate diagnosis and the most effective treatment plan.
In cases where conservative treatments are ineffective, surgical interventions such as phrenic nerve reconstruction or diaphragm pacing may be considered. These procedures aim to restore proper nerve function and improve respiratory muscle strength, ultimately enhancing the individual’s quality of life and respiratory capabilities.
The Phrenic Nerve in Medical Research
Research pertaining to the phrenic nerve continues to shed light on its intricacies and unexplored potentials.
The phrenic nerve, a crucial component of the respiratory system, plays a fundamental role in breathing by innervating the diaphragm. Recent studies have delved deep into the molecular mechanisms underlying the development and function of the phrenic nerve. Scientists have uncovered a network of genes and signaling pathways that orchestrate the formation and connectivity of this vital nerve, offering a glimpse into the intricate dance of biological processes that ensure proper respiratory function.
Recent Discoveries about the Phrenic Nerve
Recent studies have revealed fascinating insights into the phrenic nerve’s physiology and function. Researchers have identified molecular pathways and genetic factors that contribute to the development and proper functioning of the phrenic nerve. These findings have the potential to unlock new avenues for therapeutic interventions and targeted treatments for phrenic nerve-related disorders.
Moreover, cutting-edge imaging techniques have allowed researchers to visualize the phrenic nerve in unprecedented detail, providing a roadmap for understanding its complex innervation patterns and connections within the body. By mapping out the intricate neural circuitry of the phrenic nerve, scientists are paving the way for more precise interventions and personalized treatments tailored to individual patients.
Future Implications of Phrenic Nerve Research
Ongoing research into the phrenic nerve holds immense promise for advancing our understanding of respiratory disorders and improving patient outcomes. The development of innovative treatments and technologies, guided by these discoveries, may open up possibilities for better management and eventual prevention of phrenic nerve disorders. By unraveling the hidden complexities of the phrenic nerve, scientists aim to enhance respiratory health and overall well-being.
As researchers continue to unravel the mysteries of the phrenic nerve, the potential for groundbreaking discoveries in neuroregeneration and neural engineering looms on the horizon. Harnessing the regenerative capacity of the phrenic nerve may offer novel therapeutic strategies for repairing nerve damage and restoring respiratory function in patients with debilitating conditions. The future of phrenic nerve research holds the promise of transforming the landscape of respiratory medicine, ushering in an era of tailored treatments and improved quality of life for patients worldwide.
The Phrenic Nerve and Overall Health
Beyond its role in respiratory function, the optimal functioning of the phrenic nerve has implications for overall health and quality of life. The phrenic nerve, a vital neural pathway, plays a pivotal role in ensuring efficient respiratory function and overall well-being.
The Impact of Phrenic Nerve Function on Quality of Life
A well-functioning phrenic nerve enables individuals to lead an active and fulfilling life, unhindered by respiratory limitations. The ability to engage in physical activities, experience restful sleep, and maintain optimal oxygenation contributes to overall well-being and vitality. When the phrenic nerve is functioning optimally, it coordinates the contraction of the diaphragm, the primary muscle responsible for breathing. This coordinated effort ensures that the lungs receive an adequate supply of oxygen and that carbon dioxide is efficiently eliminated from the body.
However, when the phrenic nerve is compromised or damaged, it can lead to a range of respiratory issues, such as shortness of breath, shallow breathing, and decreased lung capacity. These symptoms can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, limiting their ability to engage in physical activities and causing fatigue and discomfort.
Maintaining a Healthy Phrenic Nerve
While certain factors that affect the phrenic nerve’s health may be beyond our control, there are steps we can take to support its optimal function. Engaging in regular exercise, practicing deep breathing techniques, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can all contribute to the overall well-being of this vital neural pathway.
Regular exercise, particularly activities that promote deep breathing, can help strengthen the diaphragm and improve phrenic nerve function. Activities such as swimming, yoga, and Pilates can be particularly beneficial in this regard. Additionally, practicing deep breathing techniques, such as diaphragmatic breathing, can help train the diaphragm and enhance its coordination with the phrenic nerve.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, adequate hydration, and sufficient sleep, can also support the optimal functioning of the phrenic nerve. A diet rich in nutrients, particularly those that support nerve health, such as B vitamins and omega-3 fatty acids, can help nourish the nerves and promote their proper functioning.
Furthermore, regular check-ups with healthcare professionals can help detect any potential issues early on, allowing for prompt intervention and minimizing the risk of complications. These check-ups may include tests to assess lung function, nerve conduction studies, and imaging techniques to evaluate the phrenic nerve and surrounding structures.
In Conclusion
The phrenic nerve, often overshadowed by other structures in the body, plays a pivotal role in ensuring efficient respiratory function and overall health. Appreciating its intricate anatomy, understanding its crucial role in breathing, and acknowledging the potential implications of its disorders are vital in fostering appreciation for the significance of the phrenic nerve. By continuing to explore and unravel its complexities, we can strive towards enhanced respiratory health and improved quality of life for individuals worldwide.