The Role of the Oculo Motor Nerve in Eye Movement
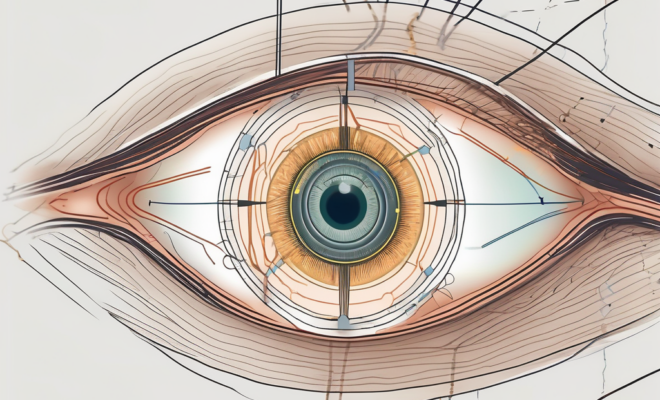
The oculo motor nerve plays a crucial role in the complex act of eye movement. This nerve, also known as cranial nerve III, controls the majority of the muscles responsible for moving the eye. Understanding the anatomy and functions of the oculo motor nerve is essential for comprehending the intricate mechanisms that govern our ability to see and interact with the world around us.
Understanding the Oculo Motor Nerve
Anatomy of the Oculo Motor Nerve
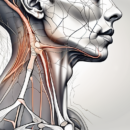
The oculo motor nerve, also known as the third cranial nerve, is a fundamental component of the visual system. Emerging from the midbrain, precisely the oculomotor nucleus, this nerve embarks on a complex journey through the intricate pathways of the skull. Its passage culminates as it gracefully enters the orbit through the superior orbital fissure, a narrow but crucial opening that serves as a gateway to the realm of ocular control.
Once inside the orbit, the oculo motor nerve branches off into a network of smaller nerves, each with a specific mission to innervate the muscles that orchestrate the symphony of eye movements. These muscles, including the medial rectus, superior rectus, inferior rectus, inferior oblique, levator palpebrae superioris, and the superior division of the superior rectus, work in harmony under the guidance of the oculo motor nerve to execute precise and coordinated motions.
The oculo motor nerve’s intricate web of connections and its meticulous control over the ocular muscles enable it to regulate not only the direction of gaze but also the speed and accuracy of eye movements. This precision is essential for tasks that demand visual acuity and coordination, such as reading fine print, tracking moving objects, and maintaining focus during dynamic activities.
Functions of the Oculo Motor Nerve
At the core of its responsibilities, the oculo motor nerve is the maestro conducting the intricate ballet of eye movements. Its primary function lies in ensuring the synchronized coordination of both eyes, a feat essential for binocular vision and depth perception. By harmonizing the actions of the ocular muscles, the oculo motor nerve facilitates seamless and fluid movements that allow us to perceive the world with clarity and depth.
Beyond its role in coordinating eye movements, the oculo motor nerve is also entrusted with the critical tasks of focusing and tracking. Through its influence on the muscles responsible for adjusting lens thickness (accommodation) and maintaining fixation on specific points, this nerve contributes significantly to the mechanisms of clear vision and visual attention. These functions are the cornerstone of our ability to shift focus between near and distant objects effortlessly, a skill that underpins many aspects of our daily visual experiences.
The Oculo Motor Nerve and Eye Movement
Coordinating Eye Movements
The oculo motor nerve coordinates the six extraocular muscles that control eye movements in various directions. These muscles work in harmony to enable movements such as horizontal and vertical gaze, convergence, and divergence. Any disruption or dysfunction of the oculo motor nerve can lead to impaired eye movements and associated vision problems.
Moreover, the oculo motor nerve plays a crucial role in maintaining binocular vision, which is the ability of both eyes to work together to create a single, unified visual image. This coordination is essential for depth perception and accurate judgment of distances, allowing us to navigate our environment effectively.
Role in Focusing and Tracking
The oculo motor nerve is responsible for controlling the ciliary muscle, which adjusts the shape of the lens to focus on objects at different distances. By contracting or relaxing the ciliary muscle, the oculo motor nerve enables the lens to change its curvature, thereby facilitating near and far vision.
Furthermore, the oculo motor nerve is involved in the pupillary light reflex, which regulates the size of the pupil in response to changes in light intensity. This reflex helps to control the amount of light entering the eye, ensuring optimal visual acuity in varying lighting conditions.
Additionally, the oculo motor nerve contributes to smooth pursuit eye movements, allowing the eyes to track moving objects accurately. This function is essential for activities like following a moving target, such as a ball in sports or a bird in flight.
Disorders Related to the Oculo Motor Nerve
The oculo motor nerve, also known as the third cranial nerve, plays a crucial role in controlling the movement of several eye muscles. When disorders affect this nerve, it can lead to a variety of symptoms that impact vision and eye coordination. In addition to the common symptoms mentioned, individuals with oculo motor nerve disorders may also experience issues with light sensitivity, eye fatigue, and headaches due to the extra effort required to focus their eyes.
Symptoms of Oculo Motor Nerve Disorders
Disorders related to the oculo motor nerve can manifest in various ways, resulting in a range of symptoms. Common symptoms include diplopia (double vision), ptosis (droopy eyelids), strabismus (misalignment of the eyes), nystagmus (involuntary eye movements), and difficulty focusing. These symptoms can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life and daily functioning.
It is important to note that oculo motor nerve disorders can occur due to a variety of reasons, including trauma, infections, vascular issues, or underlying medical conditions such as diabetes or multiple sclerosis. Proper diagnosis and management of these disorders are essential to prevent further complications and improve visual outcomes.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
When a disorder involving the oculo motor nerve is suspected, a comprehensive evaluation by a qualified healthcare professional is necessary. Diagnosis typically involves a detailed medical history, thorough physical examination, and in some cases, specialized tests such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or electrodiagnostic studies.
Treatment options for oculo motor nerve disorders depend on the specific condition and its underlying cause. Conservative management may include prescription glasses or contact lenses, prism lenses, eye patches, or visual exercises. In more severe cases, surgical intervention may be required to correct muscle imbalances and restore proper eye alignment and movement.
The Impact of Aging on the Oculo Motor Nerve
Age-Related Changes in the Oculo Motor Nerve
As we age, the oculo motor nerve undergoes natural physiological changes that can affect its function. These changes often lead to decreased efficiency in eye movements, resulting in difficulties with tasks such as reading, focusing, and tracking. Age-related changes can include a decline in muscle strength, alterations in nerve conduction, and reduced neural plasticity.
Furthermore, the aging process can also result in a decrease in the number of nerve cells and fibers within the oculo motor nerve, leading to a gradual decline in its overall performance. This reduction in nerve density can impact the coordination and precision of eye movements, making tasks that require fine motor skills more challenging for older individuals.
Maintaining Oculo Motor Nerve Health with Age
While the aging process inevitably impacts the oculo motor nerve, certain measures can help maintain its health and function. Regular eye examinations, including assessments of eye muscle movement, are essential for early detection and management of age-related changes. Additionally, engaging in eye exercises, maintaining a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and avoiding excessive eye strain can contribute to optimal oculo motor nerve health.
Moreover, incorporating specific eye movement exercises into daily routines can help strengthen the oculo motor nerve and improve its coordination abilities. These exercises may include tracking moving objects, focusing on near and distant objects to enhance flexibility, and practicing eye movements in different directions to maintain range of motion. By incorporating these exercises into a regular routine, individuals can support the health and function of their oculo motor nerve as they age.
Future Research Directions in Oculo Motor Nerve Function
Technological Advances and the Oculo Motor Nerve
Advancements in technology play a pivotal role in enhancing our understanding of the oculo motor nerve and eye movements. Novel imaging techniques, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), allow for detailed visualization and mapping of the brain regions and pathways involved in oculo motor nerve function. These advancements enable researchers to explore the intricate connections and mechanisms underlying eye movement in both normal and pathological conditions.
For example, fMRI provides researchers with the ability to observe real-time brain activity during eye movements. By analyzing the blood oxygen level-dependent (BOLD) signals, researchers can identify the specific brain regions that are activated during different types of eye movements, such as saccades or smooth pursuit. This information helps to unravel the complex neural networks involved in oculo motor nerve function.
In addition to imaging techniques, advancements in electrophysiological methods have also contributed to our understanding of the oculo motor nerve. Electromyography (EMG) allows researchers to record and analyze the electrical activity of the muscles involved in eye movement. By studying the patterns of muscle activation, researchers can gain insights into the coordination and timing of oculo motor nerve signals.
Potential Therapies for Oculo Motor Nerve Disorders
As our knowledge of the oculo motor nerve continues to expand, so does the potential for developing innovative therapies for oculo motor nerve disorders. This includes exploring neuromodulation techniques, such as transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) or transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), as non-invasive interventions to improve oculo motor nerve function.
Transcranial magnetic stimulation involves the use of magnetic fields to stimulate specific areas of the brain. By targeting the regions associated with oculo motor nerve function, researchers hope to enhance the connectivity and activity of the neural pathways involved in eye movement. Similarly, transcranial direct current stimulation applies a weak electrical current to the scalp, modulating the excitability of the underlying brain regions. These techniques hold promise for individuals with oculo motor nerve disorders, potentially improving their eye movement abilities.
Additionally, ongoing research aims to identify novel pharmacological agents that target specific pathways involved in oculo motor nerve function, potentially providing effective treatment options in the future. By understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying oculo motor nerve function, researchers can develop drugs that specifically enhance or inhibit certain neural pathways, restoring normal eye movement in individuals with oculo motor nerve disorders.
In conclusion, the oculo motor nerve plays a vital role in eye movement, coordinating the muscles responsible for precise gaze control, focusing, and object tracking. Understanding the anatomy, functions, and potential disorders related to this nerve is crucial for diagnosing and managing oculo motor nerve-related conditions. With further advancements in technology and continued research efforts, we can expect to gain deeper insights into the intricate workings of the oculo motor nerve, leading to improved diagnostic techniques and novel therapeutic approaches for individuals with oculo motor nerve disorders.